The chromatin regulatory landscape is a high-level annotation on the biological function of chromatin that combines histone modifications, transcription factor binding, and the regulatory function of genomic elements. To throughly understand the interaction of these components, researchers have developed various epigenome sequencing technologies,such as ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq. Here, prof. Yongyou Zhang provided a detailed discussion of the development of ChIP-seq & ATAC-seq and their current applications in scientific research. Finally, we provide insights into future applications and challenges.

Chromatin regulatory landscape plays a critical role in many disease processes and embryo development. Epigenome sequencing technologies such as chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) and assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq) have enabled us to dissect the pan-genomic regulatory landscape of cells and tissues in both time and space dimensions by detecting specific chromatin state and its corresponding transcription factors (Fig. 1).
Pioneered by the advancement of chromatin immunoprecipitation-chip (ChIP-chip) technology, abundant epigenome profiling technologies have become available such as ChIP-seq, DNase I hypersensitive site sequencing (DNase-seq), ATAC-seq and so on. The advent of single-cell sequencing has revolutionized the next-generation sequencing, applications in single-cell epigenetics are enriched rapidly. Epigenome sequencing technologies have evolved from low-throughput to high-throughput and from bulk sample to the single-cell scope, which unprecedentedly benefits scientists to interpret life from different angles. In this review, after briefly introducing the background knowledge of epigenome biology, we discuss the development of epigenome sequencing technologies, especially ChIP-seq & ATAC-seq and their current applications in scientific research. Finally, we provide insights into future applications and challenges.
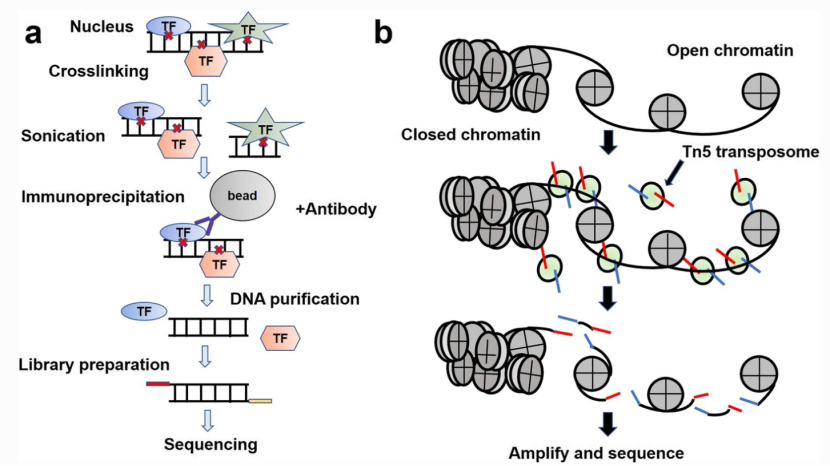
Fig. 1 Workflows of ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq.
Article Access: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43556-020-00009-w
Website for Molecular Biomedicine: https://www.springer.com/journal/43556
Looking forward to your contributions







