Recently, tumor immunotherapy based on T cells has given patients new hope, however, its problem of low response rate sometimes leads to poor prognosis. That means new strategies sensitizing cancer immunotherapy are urgently needed. Here, Rongchen Shi et al give an overview of the characteristics of tumor microenvironment, the metabolic changes of tumor‐associated immune cells, and the regulatory role of metabolic reprogramming in cancer immunotherapy.

Tumor microenvironment is a special environment for tumor survival, which is characterized by hypoxia, acidity, nutrient deficiency, and immunosuppression. The environment consists of the vasculature, immune cells, extracellular matrix, and proteins or metabolic molecules. A large number of recent studies have shown that not only tumor cells but also the immune cells in the tumor microenvironment have undergone metabolic reprogramming, which is closely related to tumor drug resistance and malignant progression. Tumor immunotherapy based on T cells gives patients new hope, but faces the dilemma of low response rate. New strategies sensitizing cancer immunotherapy are urgently needed. Metabolic reprogramming can directly affect the biological activity of tumor cells and also regulate the differentiation and activation of immune cells. The authors aim to review the characteristics of tumor microenvironment, the metabolic changes of tumor‐associated immune cells, and the regulatory role of metabolic reprogramming in cancer immunotherapy.
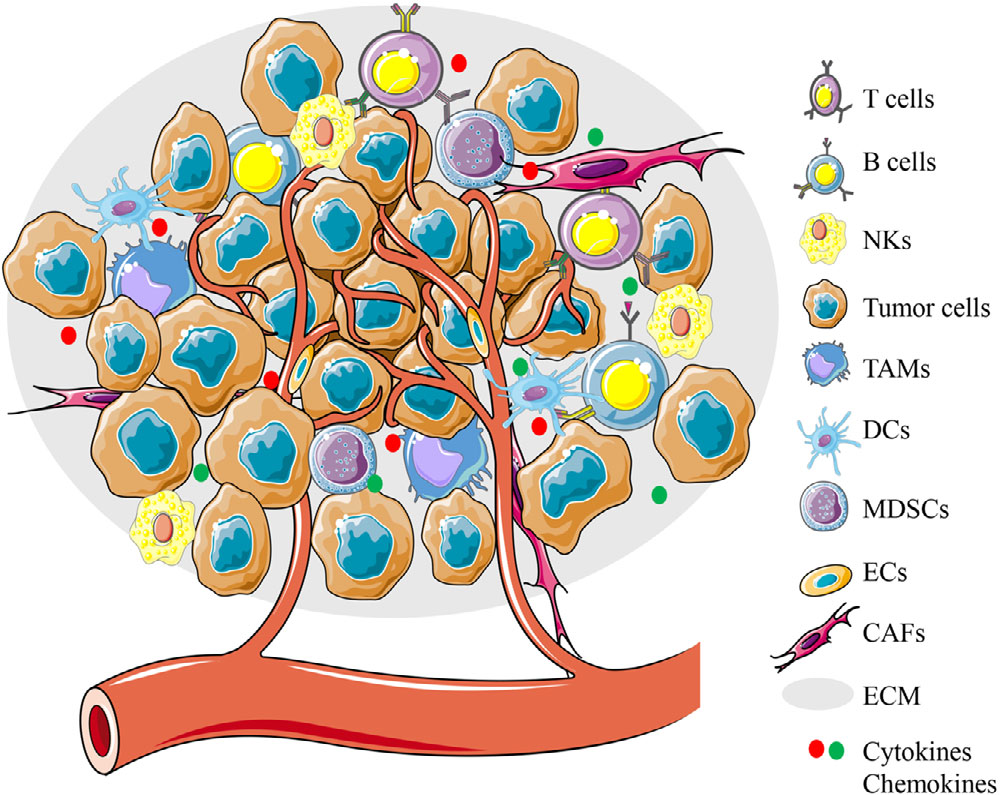
Fig. 1 Components of the TME. The TME consists of cellular and extracellular components.
Article Access:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mco2.6
Website for MedComm: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/26882663
Looking forward to your contributions.






