A closed vascular system is always established by vessel fusion. However, it has been an unsolved mystery that how vessel fusion happened in this process. In this study, Lingmiao Kong et al reported that intermedin (IMD), a calcitonin family member, promotes vessel fusion by inducing endothelial cells (ECs) to enter a “ready‐to‐anchor” state.

To create a closed vascular system, angiogenic sprouts must meet and connect in a process called vessel fusion, which is a prerequisite for establishment of proper blood flow in nascent vessels. However, the molecular machinery underlying this process remains largely unknown. Herein, we report that intermedin (IMD), a calcitonin family member, promotes vessel fusion by inducing endothelial cells (ECs) to enter a “ready‐to‐anchor” state. IMD promotes vascular endothelial cadherin (VEC) accumulation at the potential fusion site to facilitate anchoring of approaching vessels to each other. Simultaneously, IMD fine‐tunes VEC activity to achieve a dynamic balance between VEC complex dissociation and reconstitution in order to widen the anastomotic point. IMD induces persistent VEC phosphorylation. Internalized phospho‐VEC preferentially binds to Rab4 and Rab11, which facilitate VEC vesicle recycling back to the cell‐cell contact for reconstruction of the VEC complex. This novel mechanism may explain how neovessels contact and fuse to adjacent vessels to create a closed vascular system.
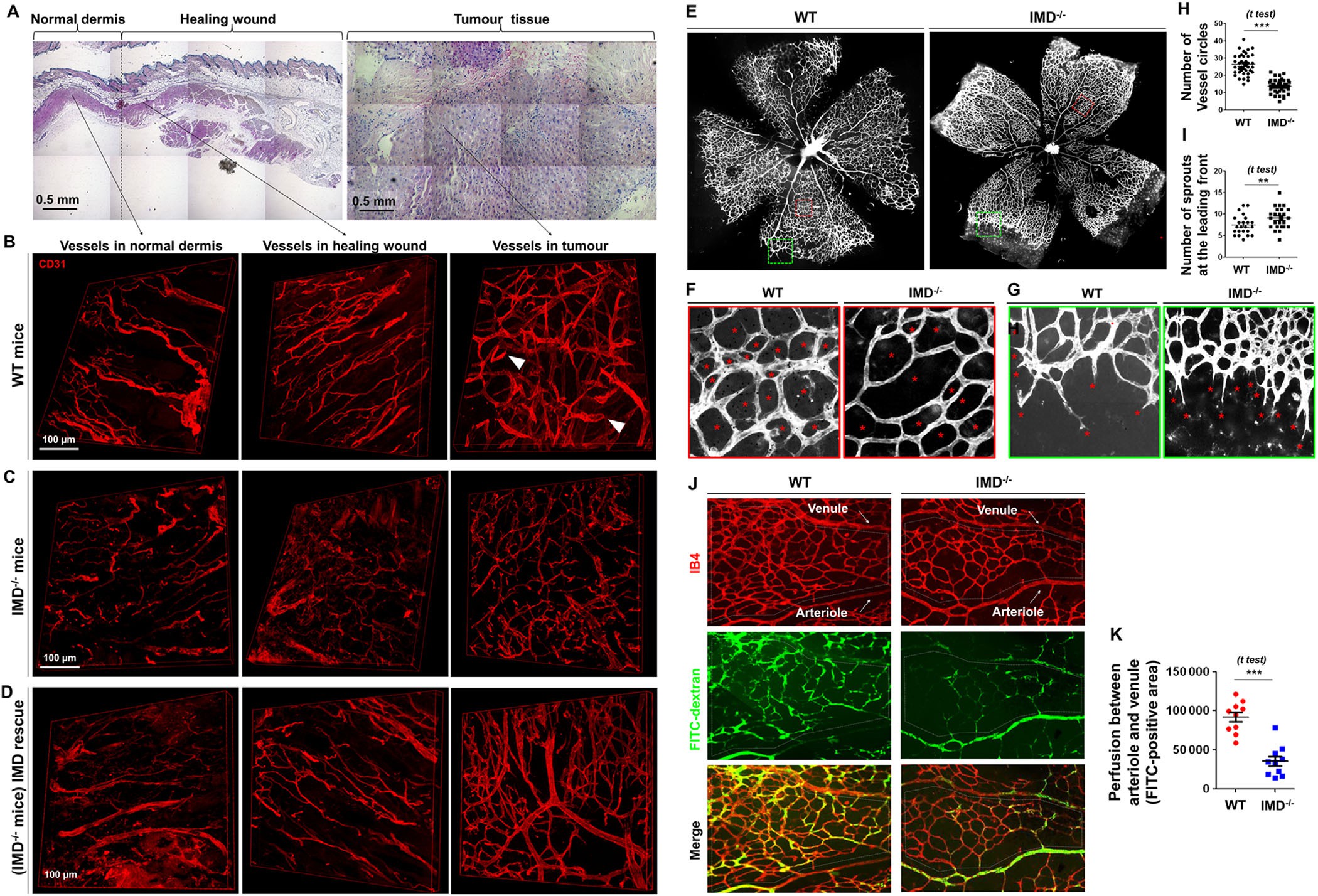 Fig. 1 IMD promotes vessel fusion in vitro and in vivo.
Fig. 1 IMD promotes vessel fusion in vitro and in vivo.
Article Access: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mco2.9
Website for MedComm: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/26882663
Looking forward to your contributions.







