On Feb.14-16, 2019, the annual ASCO-GU Cancer Symposium was hold in San Francisco, United States as expected. More than 4,400 urologists, oncologists, pathologists, imaging and other physicians engaging in the clinical and basic research of urological oncology from all over the world have an all-round, multi-perspective and in-depth academic exchanges on transformational medicine and systematic clinical diagnosis and treatment of urinary tumors. 765 related research reports are inspiring, among which 26 are from China, speaking for Chinese endeavor in urinary tumors on ASCO-GU. In addition, 10 studies from Professor Wei Qiang and Zeng Hao's teams, the Department of Urology, West China Hospital(WCH), Sichuan University(SU) contribute a lot. Hereby, I sincerely hope that we can work together with all China urology departments to interprete the research findings of the urological oncology team, WCH.

Prostate Cancer
Abs70: the diagnostic effect of multi-parameter magnetic resonance targeting prostate puncture for the people receiving the first puncture
The recent years have witnessed that the multi-parameter magnetic resonance targeting prostate puncture winning the attention of the world. Previously, the detection rate of prostate cancer guided by prostate biopsy perineal/transrectal color doppler ultrasound is not high. What's worse, the missed detection of prostate cancer with clinical significance and the detection of prostate cancer without clinical significance may delay treatment or waste medical resources. Many foresighted clinical trials prove that the fusion puncture combined prostate biopsy with multi-parameter magnetic resonance dramatically rise the defection rate of prostate cancer with clinical significance, and save, at the same time, about 20% the detection of prostate cancer without clinical significance, having the bright clinical future. Currently, due to the limitation of fusion technology and expensive fee, however, only the patients having the negative primary biopsy but their PSA keeping rising would be recommended the joint multi-parameter magnetic resonance targeted puncture so as to enhance the tumor detection rate by related guidances. As for the initial puncture of patients with suspected prostate cancer, however, the multi-parameter magnetic resonance targeted prostate cancer is controversial.
Therefore, Prof. Wei Qiang's team conducted a meta-analysis on several prospective randomized controlled clinical studies. The findings show that on one hand, as for patients having the first prostate puncture with positive magnetic resonance, joint system plus targeted puncture can maximize the detection rate of tumor but are more likely to greatly increase the detection rate of inert tumor at the same time, on the other hand, the targeted juncture alone, with fewer puncture needles, can maintain the same detection rate of prostate cancer with clinical significance(Gleason Score+4 or above) as that of system juncture.
Although the present clinical data are limited, yet we cannot get absolute evidence to support the joint targeting and system puncture or the replacement of system juncture with targeted juncture. Besides, economic benefits, patients' will and medical equipment should be taken into consideration when it turns to clinicians' decision-making. But the precision medicine is the current and future trends. With the advancement in related technologies, the era of precise targeted puncture, which can achieve the highest diagnosis effect with minimum invasiveness is bound to arrive.
Abs127: the study on coorelation between the positive midpoint of perineal prostate puncture and the positive incisal margin after radical prostatectomy
At present, radical prostatectomy is one of the standard curative treatments for localized prostate cancer among all prostate cancer treatments. But, many current studies find that there is close relation between a positive incisal margin after radical prostatectomy and the recurrence of prostate cancer. Prof. Zeng Hao's team of WCH has conducted a retrospective research on how to forecast a positive incisal edge after surgery. Previous studies show that preoperative PSA, T staging and Gleason Score have direct effects on a positive incisal edge after surgery.
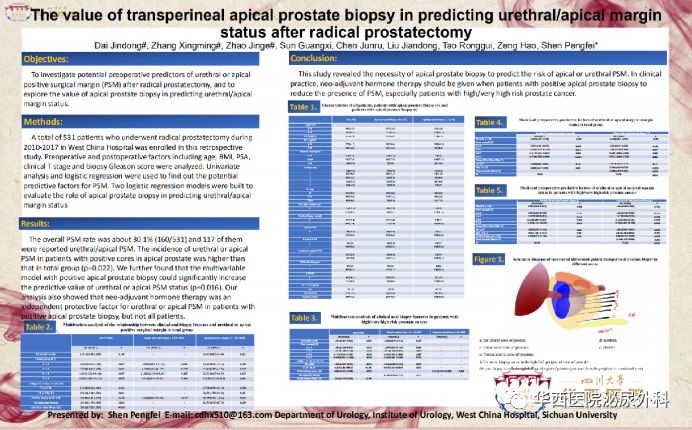
By collecting and processing data, we found that besides above factors, there is a surge in the proportion of patients with positive prostate apex and urethral incisal edge after received prostate puncture biopsy. In addition, positive apex puncture can greatly increase the accuracy of positive prostate apex and urethral incisal margin prediction model after the surgery. What's more, the subgroup analysis of patients with positive prostate apex juncture reveals that the preoperative neoadjuvant therapy can dramatically help patients to reduce the possibility of positive prostate apex and urethral incisal margin after surgery. The data of this clinical research is limited, but it does can offer valuable information that positive prostate apex juncture is of great importance to predict positive prostate apex and urethal incisal edge, and that the preoperative neoadjuvant therapy can dramatically help patients with positive prostate apex juncture, high-risk/extremely high-risk patients in particular, to reduce the possibility of positive prostate apex and urethral incisal margin after surgery.
Abs311: IL-8 protects prostate cancer cells from GSK-3beta-mediated tumor apoptosis via mTOR signaling pathway
Radical surgery and radical radiotherapy are two treatments for localized prostate cancer. Radiotherapy has the same tumor-control effect and better life quality guarantee as radical surgery, playing an increasingly important role in the radical surgery and adjuvant therapy of prostate cancer. However, there still are partial tumor cells which will build a protective mechanism themselves against radiation killing, keeping tumor cells from the harm of oxidative stress. Based on the researches of exploring relevant protective mechanisms, this study endeavors to find the possible regulatory pathways for tumor against radiation. GSK-3beta plays an important role in radiation process in accordance with some relevant reports. Radiation can stimulate body to produce a large amount of GSK-3beta so as to regulate the apoptosis of tumor cells. As a result, our research priority goes to the signaling pathways of GSK-3beta. The previous studies of Prof. Wei Qiang's team reveal that IL-8 increases in prostate cancer and that IL-8 can inhibit GSK-3beta. So we insist that the abnormal increase of IL-8 in tumor cancers lies in the self-protection of prostate cancer. Our subsequent studies prove that IL-8 can inhibit GSK-3beta's activity via phosphorylation, as a result to inhibit GSK-3beta-meditated apoptosis. At the same time, we find that mTOR signaling pathways contribute a lot in this regulating process. IL-8's regulating function lies in mTOR signaling pathway. The regulating network of IL-8 protecting prostate cancer cells from GSK-3beta-meditated apoptosis via mTOR signal pathway, therefore, may become the critical node to reverse prostate cancer cell's resistance to radiation. The interpreting of this mechanism is of clinical significance to improve prostate cancer radiotherapy.
Abs123: the study on the correlation between the detection of intraductal carcinoma of the prostate(IDC-P) in prostate biopsy specimens and pathological prognostic factors after high-risk prostate cancer radical surgery
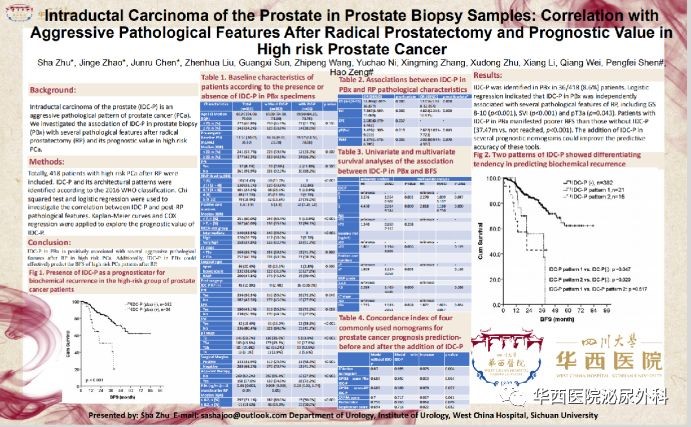
Recent years have witnessed the intraductal carcinoma of the prostate(IDC-P) being a special subtype which has drawn the attention of Prof. Zeng Hao's team. The detection of IDCP in early prostate cancer, metastatic prostate cancer and mCRPC is closely related to treatment resistance and poor prognosis. There is no reports revealing that the detection of IDC-P in needle biopsy has clinical significance for high-risk localized prostate cancer.
After analyzing the puncture speicemens and radical specimens of 418 high-risk prostate cancer patients who received PR treatment in WCH from 2010 to 2017, we found that IDC-P puncture biopsy has clear linkage with several worse pathological features(Gleason Score 8-10, seminal vesicle invasion, pathological T stage) in radical specimens and is the independent prognostic indicator predicting worse survival outcome indicators. Based on that, we add IDC-P, an independent influential factor, to several current localized prostate cancer prognostic evaluation scales(D’Amico nomogram, GPSM score, CAPRA score, Partin table and Stephenson score) for predicting ability test. We found that IDC-P can greatly enhance predictive performance in all predictive scales. Built on all researching findings above, we can establish targeting and effective clinical treatment strategies in advance to enhance the overall efficacy of high-risk prostate cancer patients with IDC-P by taking advantage of IDC-P detection information in puncture specimens.
Abs117: the regular Gleason Score and innovative precise diagnosis of prostate cancer
With the development of the times, accurate assessment and treatment for tumor is crucial for patients's good prognosis. As a result, the interpreting of prostate cancer Gleason scoring system should follow the current trends and keep refining and improving. Prof. Wei Qiang's team, WCH engaged in an in-depth interpreting of prostate cancer pathological diagnosis score and conducted correlation study on three-levels of Gleason Score and the prognosis of patients with prostate cancer. In this way, clinicians can choose the most suitable treatment and more thorough prognosis judgment in terms of diagnose and treatment.
Though this study needs more clinical data to supplement, it still can offer useful messages that a Gleason score of 5 in its three-levels is closely connected with patients' biochemical recurrence. This finding is crucial to patients with low-risk/high-risk prostate cancer because the appropriate systematic treatment strategies will increase patients' curability of tumor. Of course, just as the discussion in ASCO-GU, accurate diagnosis and treatment are closely related to patients, which is the priority of medical researchers and workers as well as Chinese patients.
Abs128: the verification of ISUP2014 grouping system in patients with high-risk localized prostate cancer
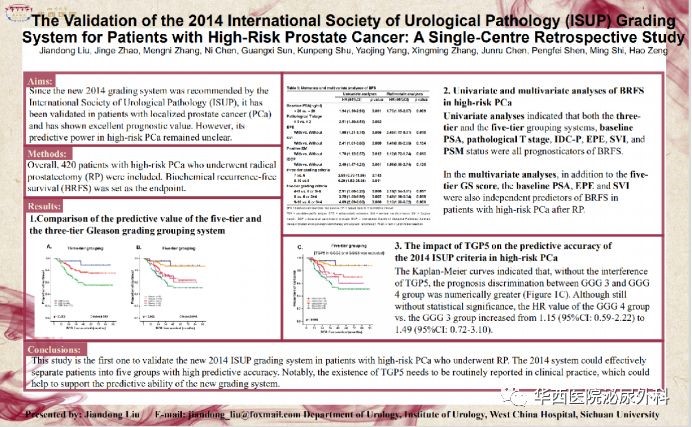
In 2014, International Society of Urological Pathology(ISUP) updates Gleason Score based on ISUP 2005. It divides prostate cancer patients into five groups according to Gleason score, namely, GS 3+3,GS 3+4, GS 4+3, GS 8, GS 9-10. Later, a series of confirmatory studies have prove the advantages of five groups in ISUP 2014 for all prostate cancer patients. having verified the new classification system of ISUP's prediction limitation in patients, Prof. Zeng Hao's team casts their eyes to the confirmation of ISUP 2014 grouping system's prediction ability in high-risk localized prostate cancer patients.
In the western region of China, prostate cancer patients generally have a late pathological stage than that of patients in developed countries of Europe and America as well as that of patients in the eastern region and westerners are more likely to suffer high-risk prostate cancer. It is, therefore, to verify the new version scoring system's prediction ability among high-risk populations. This research contains 420 high-risk localized prostate cancer patients who received radical prostatectomy from WCH. The finding reveals that ISUP2014 classification system can distinguish the prognosis difference between GS 3+4 and GS 4+3. But the system is limited in distinguishing patients' prognosis between GS 4+3 and GS 8. The subgroup analysis reveals that the proportion of Tertiary Gleason pattern 5, (TGP5) in GS 4+3 type patients is 27%, much higher than 7.5% in GS 3+4 type patients. By excluding the interference of TGP5 in GS 4+3 group, the prognosis differences between GS 4+3 group and GS 8 group are increasing, which also partially proves the finding of Abs117. The study proves that though ISUP 2014 grouping system's prediction ability performs badly in high-risk localized prostate cancer patients than that of primary localized prostate cancer patients, yet it good prediction ability can guide clinicians' prognosis judgments on patients. As for the judgments on high-risk patients prognosis, the evaluation of Tertiary Gleason Score, apart from ISUP scoring system, together with other clinical pathological parameters affecting the prognosis of high-risk patients is worthy of clinicians' attention. The prediction scale/model integrating various parameters is a better evaluation way.
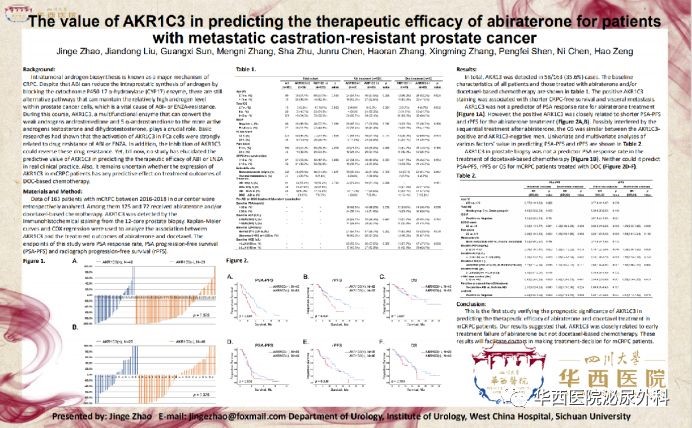
Abs313: the prognosis and therapeutic predicting value of AKR1C3 expression in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer(mCRPC) in prostate biopsy specimens
The metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer(mCRPC) is the terminal stage of prostate cancer. The new endocrine therapy represented by abiraterone and enzalutamide and the cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs represented by docetaxel constitute the golden standard for treatment of mCRPC. Almost all the drugs for mCRPC, however, play a limited role in expanding patients' life span. On the basis of lacking better treatment strategies, how to provide individualized treatment for each mCRPC patients is the best way to maximize the efficacy of these drugs. The detection of AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells(CTC) seems to allow us to see the criteria for finding patients of new endocrine therapy, but later studies have found that AR-V7 is costly but its specificity isn't specific enough to meet our expectation. New biomarkers and easy-to-use detection methods are still worth exploring. Prof. Zeng Hao's team conducted researches on different possible molecular mechanisms causing docetaxel or neoendocrine therapy resistance and engaged in the finding of new makers predicting mCRPC patients' efficacy, which is essential to enhance mCRPC efficacy so as to eventually improve patients living.
AKR1C3 is a key enzyme in the endogenous androgen synthesis pathway of prostate cancer tumors. Our early studies reveal that the positive expression of AKR1C3 in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer tissues is related to patients' short occurrence time of CRPC. Taking advantage of the two-times puncturing tissue of prostate cancer primary lesions and/or puncturing tissues of metastatic lesions, this study investigates the expression pattern of AKR1C3 in mCRPC tissues and its effect on the therapeutic effect of abiraterone or docetaxel. It turns out that the positive rate of AKR1C3 is as high as 35.6% among 163 patients who received abiraterone or docetaxel and had two-times puncture tissue. Survival analysis shows that positive expression of AKR1C3 is closely related to shorter PSA progression-free survival and imaging progression-free survival among patients receiving abiraterone treatment. That result is further validated in a subgroup analysis based on patients' each clinical pathological indexes . However, the expression of AKR1C3 has no relation to the therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel. This study suggests that a second puncture of the primary lesion for mCRPC patients and an immunohistochemical examination of AKR1C3 may help clinicians to optimize the selection of first-line treatment. We should be alert when choose abiraterone as the first choice of treatment for patients with positive AKR1C3, those combined with negative AR-V7 in particular. Combined targeted therapy against AKR1C3 may improve the sensitivity of this type of patients to new endocrine therapy, which requires exploration in this direction.
Renal Cell Carcinoma
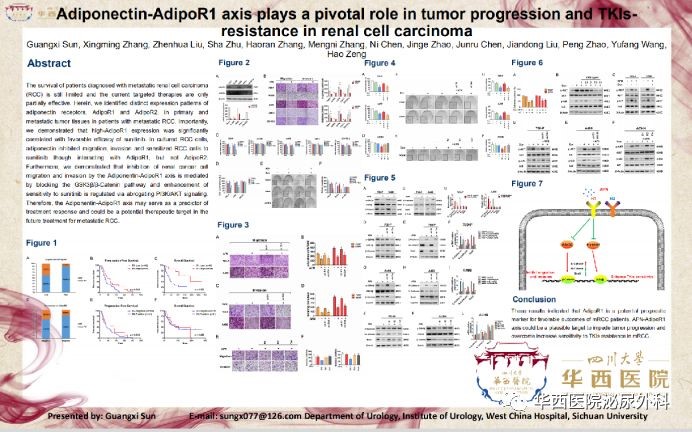
Abs634:Adiponectin-AdipoR1 axis plays a pivotal role in tumor progression and TKIs-resistance in renal cell carcinoma
TKIs targeting angiogenesis-related molecules is the first-line treatment for patients at the terminal stage of kidney cancer. But TKIs usually bring many adverse reactions to patients and almost all patients will develop TKIs-resistance after receiving treatment for about 12 months. Prof. Zeng Hao's team began with clinical, explored the TKIs-resistance mechanism in advanced kidney cancer and found the key molecules of TKIs-resistance. The efficacy of TKIs can be significantly enhanced by targeting the molecule and its related signaling pathways, which provides new therapeutic strategies and ideas for ultimately improving the prognosis of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
We found that the expression of APN receptor AdipoR1 may indicate efficacy via immunohistochemical staining of primary and/or metastatic lesions in 126 patients with advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received TKIs treatment in WCH from 2008 to 2016. Compared with patients having low expression of AdipoR1, the PSF and OS are greatly prolonged in patients having high expression of AdipoR1. The vitro experiments also further verifies the clinical findings that APN can inhibit the invasion and migration of renal cancer cells by activating AdipoR1 to block PI3K/AKT/NF-κB and GSK3β/β-catenin pathways respectively and increase the sensitivity of cancer cells to TKIs. Therefore, clinical detection of AdipoR1 expression in tumor tissues may assist to predict the efficacy of TKIs in patients with advanced metastatic kidney cancer. As for patients with low expression of AdipoR1 in tumor tissues, the efficacy of TKIs can be enhanced by targeting AdipoR1 and activating APN-AdipoR1 signal axis.
Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma (UTUC)
Abs452: the effect of preoperative metabolic syndrome on the prognosis of patients with UTUC
The occurrence of metabolic syndrome is attributed to personal dietary habit and lifestyle. Its diagnostic criteria include obesity, hypertension as well as abnormal lipid metabolism and glucose metabolism. In accordance with previous studies in colorectal cancer, renal cell carcinoma and prostate cancer, patients with metabolic syndrome have lower overall survival rates than patients without metabolic syndrome, but whether metabolic syndrome affects the prognosis of patients with UTUC lacks attention all the time.
Prof. Wei Qiang's team collected the clinical data of 644 UTUC patients in WCH from 2003 to 2016 and analyzed the possible effects of metabolic syndrome on the prognosis of UTUC patients. The finding reveals that the correlation analysis shows metabolic syndrome is independently associated with UTUC high-grade tumors, T staging and lymphatic vessel invasion in 157/644 (24.4%) patients with UTUC had metabolic syndrome. Multivariate regression analysis shows that metabolic syndrome is an independent risk factor for tumor-specific survival of UTUC patients after surgery[HR 1.38,95%CI:1.01-1.88, P=0.042]. Subgroup analysis also reveals that patients with metabolic syndrome had worse disease progression-free survival, tumor-specific survival and overall survival among non-muscular-invasive UTUC patients.
Till now, this article is the first one in the world to study the prognosis of metabolic syndrome and UTUC with large sample size. Our findings reveal that preoperative assessment of whether UTUC patients are in the state of metabolic syndrome or not is necessary and that the assessment may assist clinicians to predict the patients prognosis more accurately and develop effective interventions to improve patient survival. The single-center retrospective study is, of course, a major flaw in this study, yet high-quality studies with multiple centers, large samples and longer follow-up are needed to further confirm our findings.
Abs414: the disease prediction model assists in the diagnosis and treatment of UTUC patients.
UTUC Asian populations embody unique characteristics due to the exposure of various risk factors such as the environment and traditional Chinese medicine. UTUC accounts for about 5% of all urothelial carcinomas in Western countries while it accounts for about 20-30% of all urothelial carcinomas in China. In recent years, that related indicators in perioperative period have a significant impact on the prognosis of UTUC is confirmed by Prof. Wei Qiang's team and a large number of studies both home and abroad. Currently two teams from North America and Europe have constructed prognostic prediction models for patients after RNU respectively, but their models didn't take these perioperative indicators into account. So, it is essential to include these indicators in the prediction model for analyzing and to establish a prediction model suitable for the Chinese population. By analyzing and screening UTUC patients who received RNU treatment in WCH from 2003 to 2016, the research team established an UTUC prognostic prediction model. The model shows better prediction ability after adding perioperative relevant indicators. It will provide the consultation, follow-up and risk classification for patients as well as important clinical guidance for patients with different risk classifications when selecting adjuvant therapy.
The 2019 ASCO-GU has already ended. During the meeting, we experienced the latest idea and advancement in urology oncology and witnessed the latest contributes from China and other Asian counties as well as recognized the mission of China's urology oncology treatments. I sincerely wish we can have a better performance next year.