The world is faced with the second epidemic impact. For China, will there be a second impact as well? How long do we still have to wear masks? How long will the epidemic continue? The stall and booth market is popular again these days, but is it safe for us to go shopping in the nighttime market? Now that students have come back to school, is the campus safe? What implications does this epidemic bring to the public health system? With the advent of the 5G era, what black technology can be used for remote consultation of severe MDT? These are issues that we pay close attention to for quick solutions.

On June 8th, sponsored by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association, Healthy China Action Innovation & Development Alliance and West China Hospital of Sichuan University, and supported by scgc.sctv.com and Healthy China TV, a special TV live featuring program, Medical Approach • Doctor Talks about Medical, invited Professor Kang Yan, director of the Department of Intensive Medicine of West China Hospital of Sichuan University, leader of the third batch of the medical aid team for Hubei from West China Hospital, and one of the experts of the "Eight Immortals for Critical Care", shared his 96 days battle against COVID-19 on the frontline with the theme of "‘Black Technology’ for Critical Care Consultation in 5G Era", including his assisting of Wuhan, Suifenhe and Mudanjiang consecutively. Focusing on the application of new technologies during the epidemic combat, he told the audience of situation in the frontline and popular science on protection via online live featuring.

Professor Kang Yan in front of Hongqi Hospital
On February 7th, Professor Kang Yan, leader of the third batch of medical aid team for Hubei from West China Hospital of Sichuan University, led a medical team of 130 members to support Wuhan. After working in Wuhan for 60 days, he returned to Chengdu on April 7th. After three days of rest, he set off to Suifenhe, Heilongjiang province. On May 16th, Professor Kang Yan, who had been fighting for 96 days away from home, returned to Chengdu for two weeks of quarantine. Talking about his aid in Suifenhe in Wuhan and Heilongjiang, Professor Kang said that his work in Wuhan was an "encounter war" where he was faced with crises and dealt with them in emergency. His work in Heilongjiang was a targeted "blocking battle", because with the experience of Wuhan, he was fully prepared for the challenge in Heilongjiang, both in terms of materials and plan. At present, the domestically transmitted cases of COVID-19 in the country have been terminated, and new added cases are all imported. With the experience in Wuhan, both administrative departments and medical institutions across the country are able to prevent and treat COVID-19 in a steady and orderly manner.
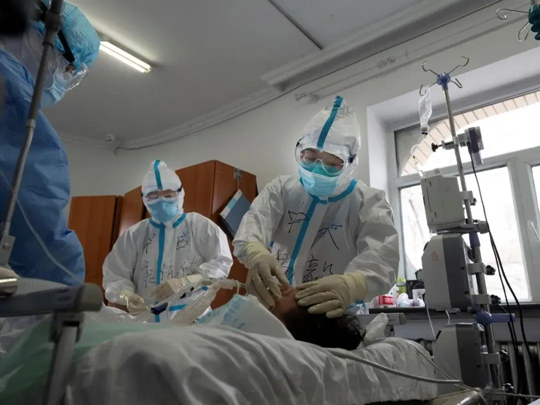

Professor Kang Yan treats patients in hospital
Many people were worried about Suifenhe and Mudanjiang in Heilongjiang, but Professor Kang Yan found that local administrative departments and medical institutions did a great job in preventing COVID-19. Upon his arrival in Suifenhe, the first three experts from Professor Kang's team conducted a survey in Suifenhe People's Hospital and local quarantine sites. They also discussed the measures and strategies for the prevention of imported cases with the leaders of local and National Health Commissions. The Mudanjiang Hongqi Hospital was designated as the hospital to receive COVID-19 patients, and within a short of time, 1,000 regular COVID-19 patient beds, 130 critical patient beds and a makeshift hospital of 600 beds were established for the prevention and treatment of first batch of people returning from abroad. In terms of treatment, Professor Kang implemented a "graded treatment" system, allocating medical resources according to the illness degrees of the patients. For critically ill patients, more treatment, more monitoring, and more support were needed to maximize the chance of survival; for patients with moderate symptoms, efforts were mainly made to manage the patient's existing illnesses; for patients with mild symptoms, efforts were made on comforting them. Targeted treatment was conducted for different patients situations.

Professor Kang Yan takes picture with cured COVID-19 patients in the ward
Speaking of imported cases and asymptomatic carriers, Professor Kang said that at present, imported cases are already blocked in going through the customs. For regions free from domestically transmitted cases, administrative departments and medical institutions at all levels have already formulated plans to prevent the recurrence of large-scale disease transmission, and made preparation for medical supplies and personnel. The temperature measurement required to enter and exit different places can ensure the safety of most people, and therefore we should not fall into panic as before. The epidemic is now normalized, where prevention and treatment are equally important. Regarding both the prevention of individual cases and group cases, only by emphasis on prevention and treatment can we reduce the risk of infection and the pressure of epidemic combat. In Hubei's "encounter war", the most important measure was to establish makeshift hospitals to gather confirmed patients for quarantine and treatment, which greatly reduced the risk of outward transmission and prevented more people from catching the disease.
Professor Kang Yan in Medical Approach Live Streaming
"Inspiration" from the Epidemic
What inspiration has this epidemic brought to the public health system? Professor Kang said: In this epidemic, the makeshift hospital has played a very prominent role. At present, the government is considering extending more functions to deal with public emergencies, such as water, electricity, gas, and even oxygen supply in newly built large buildings. Such buildings have their everyday functions, and in case of an emergency, they can serve as quick response sites.
What is "critical care medicine" after all?
In order that people can establish some understanding of critical care medicine, Professor Kang popularized "what is critical medicine?", "Does entry to ICU mean no hope of survival?", etc. The Department of Critical Care Medicine is mainly to provide support for the rescue and life extension of critically ill patients; to provide support for the treatment and organ function of patients with multiple organs dysfunction; to prevent and treat multiple organs dysfunction syndrome. The Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a hospital's medical unit that collectively monitors and treats critically ill patients. It is responsible for providing timely, comprehensive, systematic, continuous, and rigorous monitoring and treatment of critically ill patients. ICU gathers together critically ill patients in the hospital, professional medical staff, and modern monitoring and treatment equipment, with the goal to increase the success rate of critical patient rescue and reduce mortality. "Care" in the "Intensive Care Unit" means, on the one hand, "monitoring", and on the other hand, "rescue". In other words, it conducts continuous bedside monitoring on the condition with monitoring instrument, and makes corresponding treatment decisions in a timely manner according to the change of the condition to save the lives of critical patients to the greatest extent and to improve their life quality. The successful rescue rate of the ICU ward is about 90%, so it plays an important role in medical treatment.

Professor Kang Yan in the Medical Approach live streaming
5GMDT remote diagnosis and treatment
In this epidemic outbreak, 5GMDT remote diagnosis and treatment played an important role. What is 5GMDT remote diagnosis and treatment? 5GMDT remote diagnosis and treatment refers to remote consultation and collaboration of multi-disciplinary teams via 5G technology. Experts in various departments jointly formulate the best treatment plan for patients through discussion to ensure high-quality diagnosis and treatment recommendations and treatment plans. Professor Kang said that during the epidemic outbreak, expert teams from different medical departments across the country conducted remote consultations through the 5GMDT system every day.
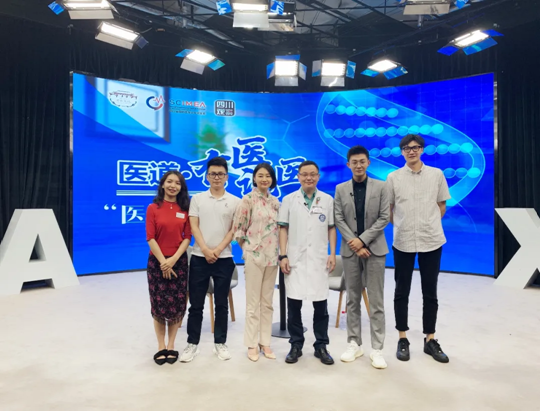

Professor Kang Yan takes a picture with the staff of Medical Approach and Zhang Mengfan, Secretary-General of Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association
At the end of the program, Professor Kang said that the epidemic is not over yet, and therefore China still needs to maintain high vigilance. He hopes that people can carry on the prevention and control measures.
This time, Medical Approach • Doctor Talks about Medical was featured live on scgc.sctv.com, thecover.cn, Sina Weibo, youku.com, toutiao.com, ixigua.com and other platforms. It was jointly released by people.com.cn, qq.com, sina.com, ifeng.com, etc., with a total of over 1.5 million viewers.






