In recent years, the tumor-derived exosome has been perceived as a hot and emerging biomarker for various cancers diagnosis and management in non-invasive manner. However, the problem of exosome isolation and detection hinder the application of exosomes. In the review newly published by Molecular Biomedicine, authors summarized the recent progress on exosome associated tumor biomarkers and some new technologies for exosome isolation and detection and also discussed future direction of exosome analysis methods.

Exosomes are secreted by cells and are widely present in body fluids. Exosomes contain various molecular constituents of their cells of origin such as proteins, mRNA, miRNAs, DNA, lipid and glycans which are very similar as the content in tumor cells. These contents play an important role in various stages of tumor development, and make the tumor-derived exosome as a hot and emerging biomarker for various cancers diagnosis and management in non-invasive manner. The present problems of exosome isolation and detection hinder the application of exosomes. With the development of exosome isolation and detection technology, the contents of exosomes can be exploited for early cancer diagnosis. This review summarizes the recent progress on exosome associated tumor biomarkers and some new technologies for exosome isolation and detection, including viscoelasticity-based microfluidic system (Fig. 1), acoustofluidics-based isolation method (Fig. 2) etc. Furthermore, the future development direction in exosome analysis methods is also discussed.
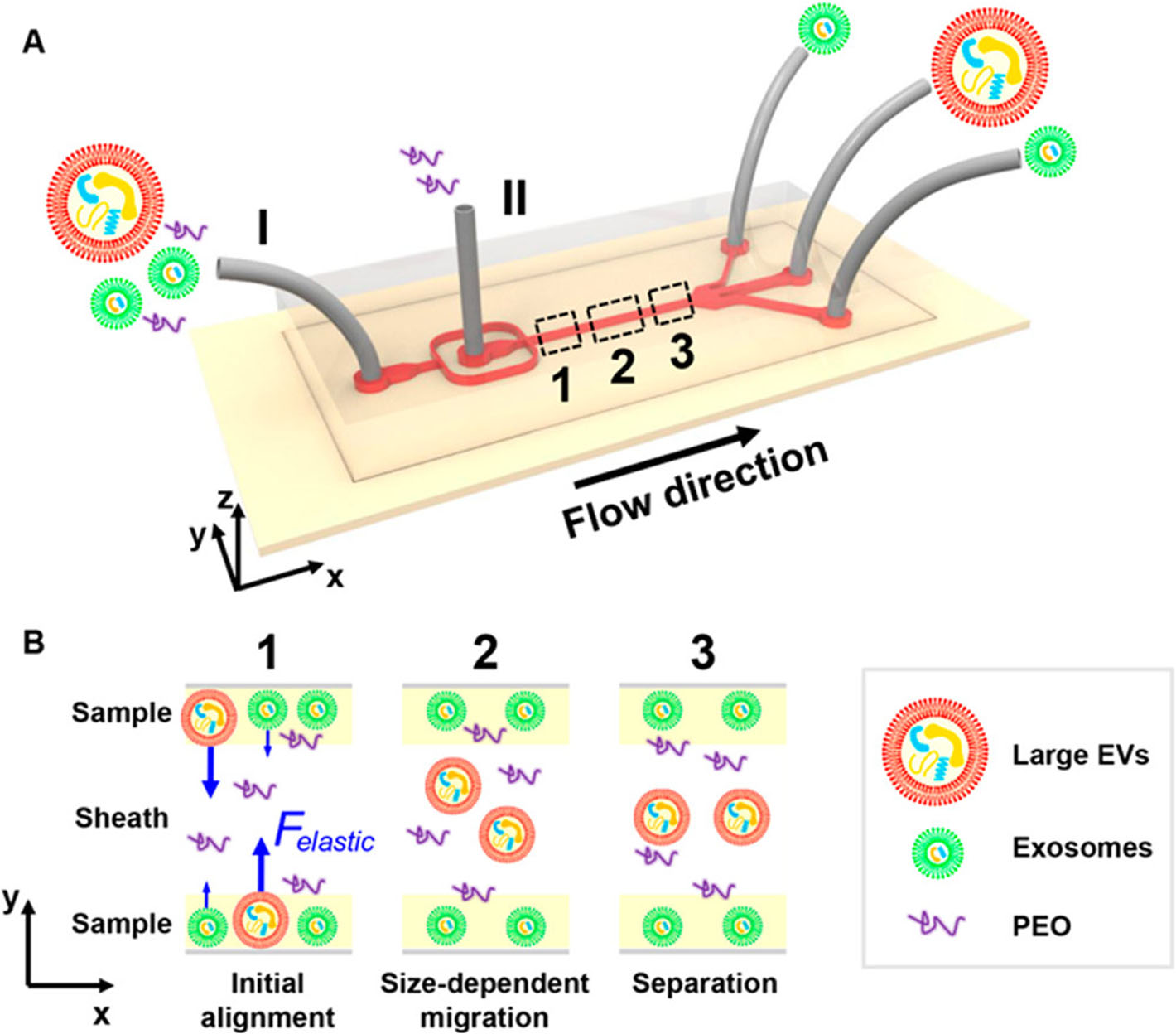
Fig. 1 The microfluidic chip for exosome separation from large EVs
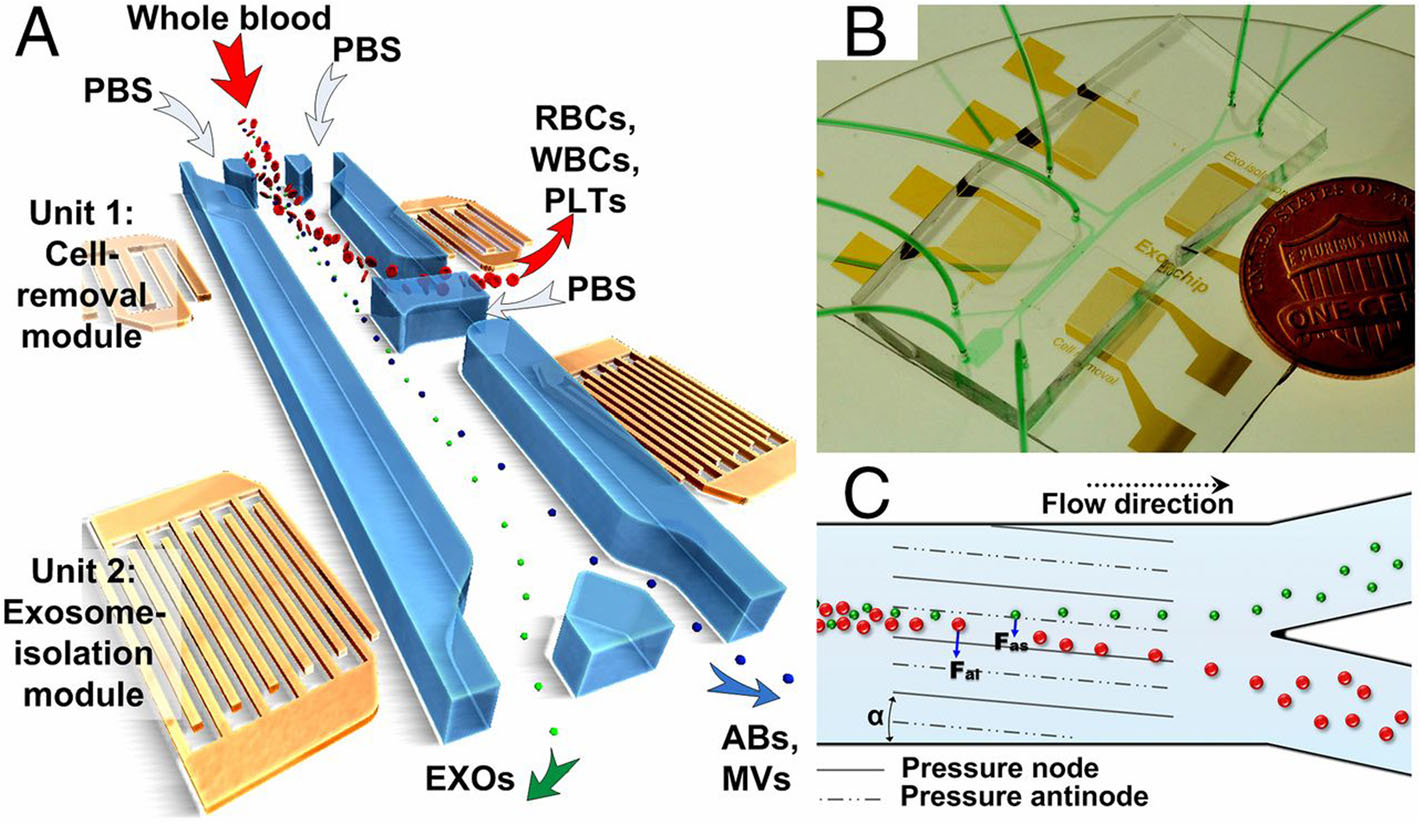
Fig. 2 The platform underlying integrated acoustofluidic device for isolating exosomes
Article Access: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43556-020-00002-3
Website for Molecular Biomedicine: https://www.springer.com/journal/43556
Looking forward to your contributions







