The effects of cGAS/STING in defenses against infection and autoimmune diseases have been well studied, still it is worthwhile to discuss the roles of cGAS/STING pathway beyond the “classical” realm of innate immunity. In the present review, researchers summerized the role cGAS/STING pathway plays in various pathological and physiological process and emphasized its involvment in some “nontraditional” way.

Cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and innate immune response initiator. Binding with exogenous or endogenous nucleic acids, cGAS activates its downstream adaptor, stimulator of interferon genes (STING). STING then triggers protective immune to enable the elimination of the pathogens and the clearance of cancerous cells.
Recent studies have revealed its involvement in non-canonical inflammasome formation, calcium hemostasis regulation, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response, perception of leaking mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), autophagy induction, cellular senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) production, providing an exciting area for future exploration. Previous studies generally focused on the function of cGAS/STING pathway in cytoplasm and immune response. In this review, the authors summarize the latest research of this pathway on the regulation of other physiological process (Fig. 1) and STING independent reactions to DNA in micronuclei and nuclei. Together, these studies provide a new perspective of cGAS/STING pathway in human diseases.
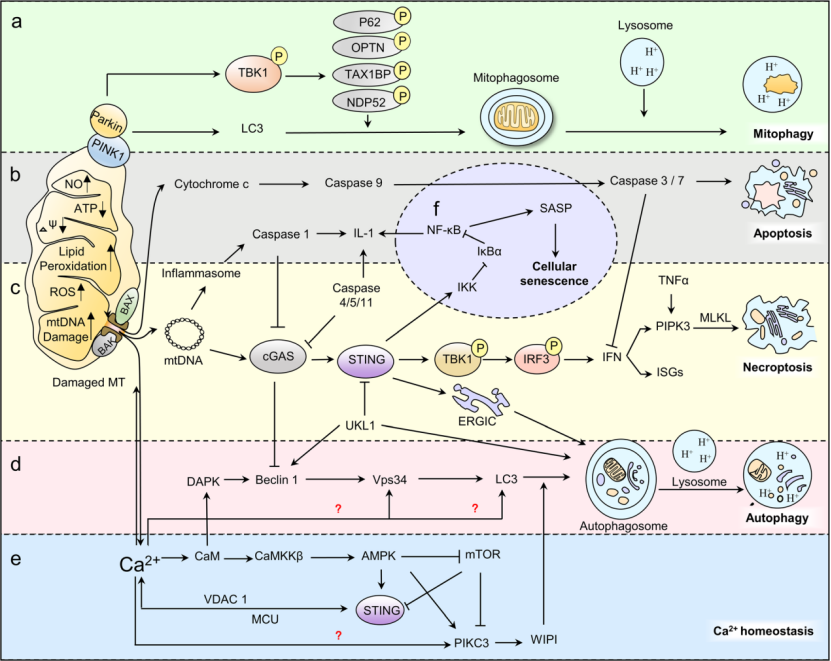
Fig. 1 Regulatory role of cGAS–STING pathway in physiological processes. cGAS/STING participates in regulating mitophagy
Article Access: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43556-020-00006-z
Website for Molecular Biomedicine: https://www.springer.com/journal/43556
Looking forward to your contributions







